3D Printing Process Overview
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary process that creates physical objects from a digital design. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that often involve cutting away material to create the desired shape (subtractive manufacturing), 3D printing adds material layer by layer to build the object. This technology has applications in various fields, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, fashion, and consumer goods, offering unparalleled flexibility in design and production
How does 3D printing work?
The 3D printing process begins with a digital model of the object to be printed. This model is typically created using computer-aided design (CAD) software or obtained from a 3D scan of an existing object. Once the digital model is ready, it's converted into a printable file format, such as STL or OBJ, that a 3D printer can interpret.
Step 1: Design
CAD Modeling: The first step is to create a 3D design using CAD software. The design is saved in a file format compatible with 3D printing. If you do not have a design, we may be able to design the part or we can work with industry professionals on your behalf. Of course, your intellectual property is secure with us, and we will provide an NDA upon request.
Step 2: Slicing
Slicing Software: Before printing, the design file must be "sliced" into thin horizontal layers using slicing software. This software also allows for the adjustment of printing settings, including layer height and print speed.
Step 3: Printing
Layer-by-Layer Construction: The 3D printer reads the sliced file and prints the object layer by layer. The material used can vary widely, including plastics, resins, metals, and even living cells, depending on the printer type.
Step 4: Post-Processing
Cleaning and Curing: After printing, some objects require post-processing steps such as cleaning off support material or curing under UV light to reach their final form and strength.
Types of 3D printing technologies
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This is the most common type of 3D printing, where a thermoplastic filament is heated and extruded through a nozzle, layer by layer, to build an object.
Stereolithography (SLA): SLA uses an ultraviolet laser to harden liquid resin into solid plastic, layer by layer, to create highly detailed objects.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): In SLS, a laser sinters powdered material, typically nylon or polyamide, to form solid objects without the need for support structures.
Advantages of 3D printing
Customization: 3D printing allows for high levels of customization without significantly increasing costs.
Complexity: It enables the production of complex and intricate designs that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
Speed: Rapid prototyping with 3D printing accelerates the design and development process.
Waste Reduction: Additive manufacturing reduces waste by using only the material needed to create the object.
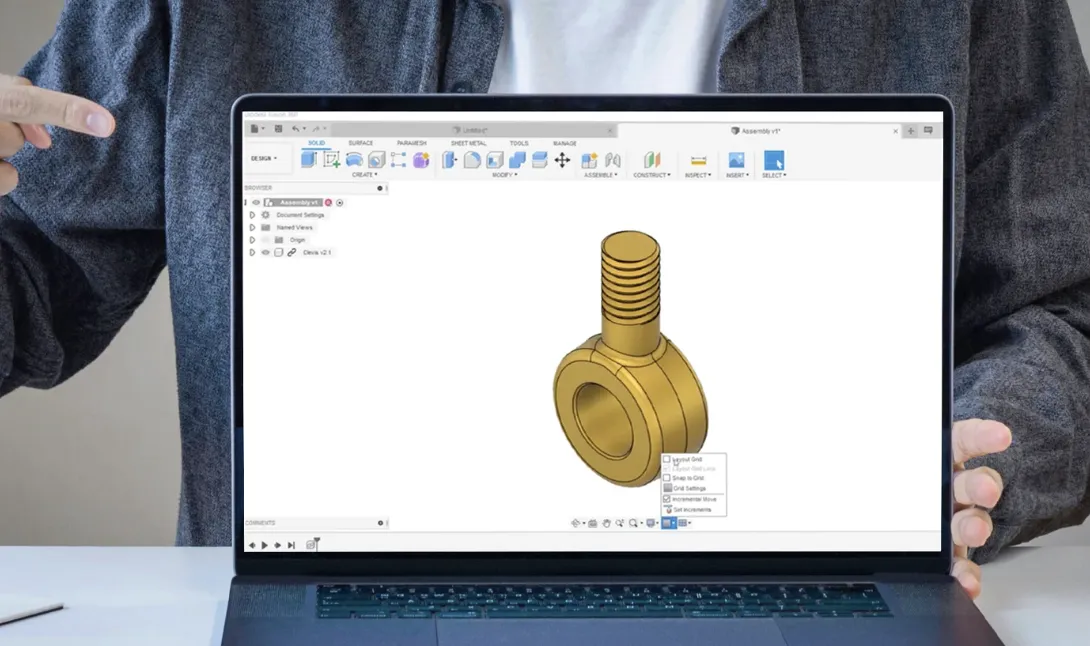
CAD Design and 3D Sculpting
Combining CAD Design's technical precision with 3D Sculpting's artistic detail, we swiftly transform initial sketches into detailed digital models. These models are then brought to life through advanced 3D printing, materializing concepts into tangible objects with speed and efficiency. This streamlined process showcases the synergy between digital design and physical manufacturing, ideal for rapid prototyping and custom creations.
We can transform your simple picture into a sophisticated 3D design today!
3D Printing Services List
Experience true cutting-edge 3D technology with our range of services at Innova 3D, LLC. where innovation meets practicality, ensuring every creation is not just a print but a masterpiece of precision and quality.
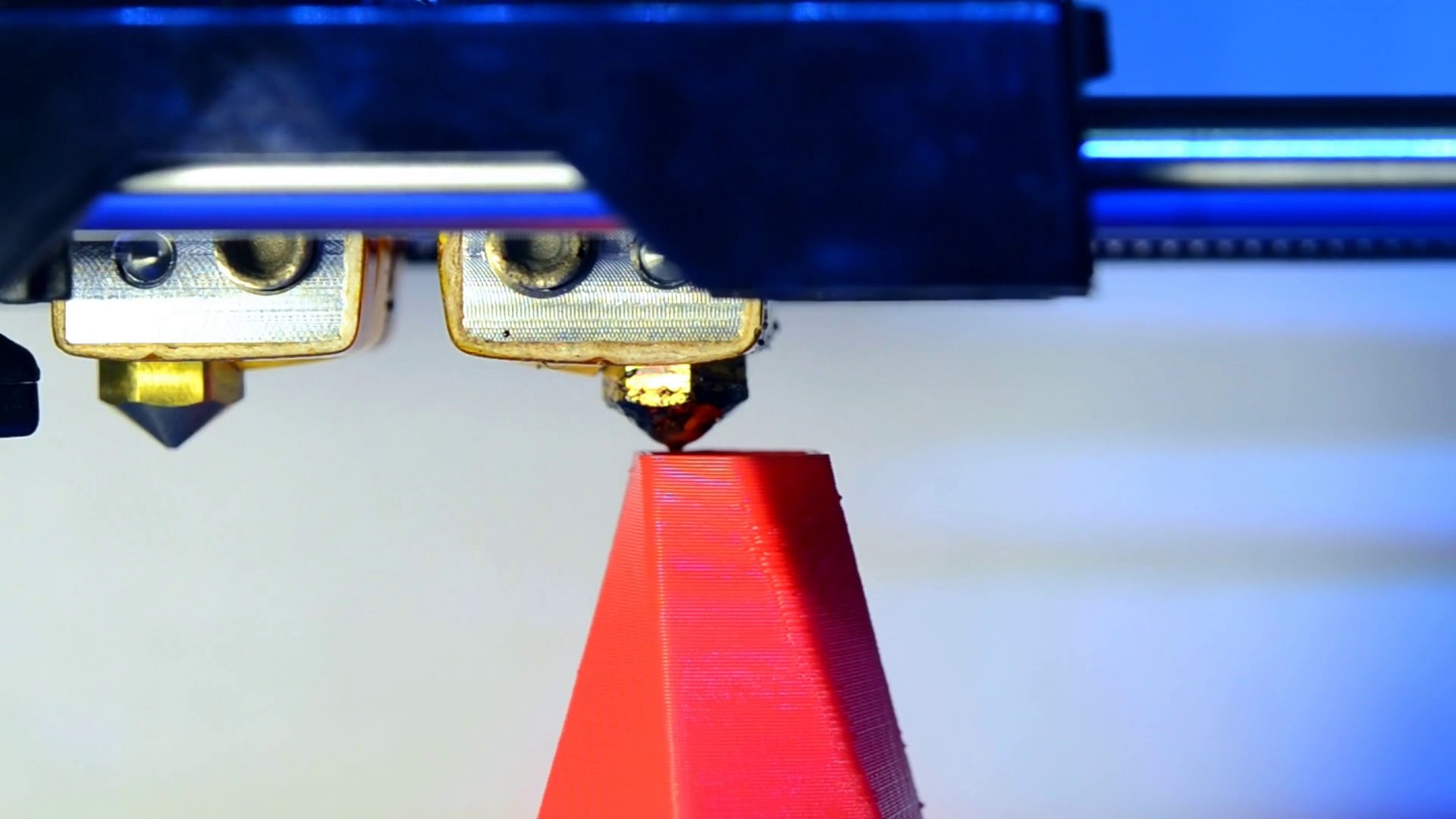
Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
FFF is a 3D printing process that involves feeding a continuous filament of thermoplastic material through a heated extruder. In this method, the filament is melted and extruded layer by layer to construct a three-dimensional object. This technique is notable for its versatility and ease of use, making it popular for both hobbyist and professional applications in creating detailed, customizable objects.
We support a broad range of 3D printing materials including PLA, ABS, ASA, Polycarbonate, Carbon Fiber, Nylon, PETG and more.

High Definition Printing Utilizing SLA (Stereolithography)
SLA is a 3D printing technology that uses a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic in a process called photo polymerization. This method allows for extremely high-resolution printing, capable of producing parts with fine details and a smooth surface finish. SLA is particularly favored for applications that require precise geometries and intricate details, such as dental work, jewelry design, and prototyping for various industries.
We include the following for service:
FormLabs Clear Resin, FormLabs Flexible Resin, FormLabs Elastic Resin, FormLabs Tough Resin, FormLabs Draft Resin.

CAD Design and 3D Sculpting
Combining CAD Design's technical precision with 3D Sculpting's artistic detail, we swiftly transform initial sketches into detailed digital models. These models are then brought to life through advanced 3D printing, materializing concepts into tangible objects with speed and efficiency. This streamlined process showcases the synergy between digital design and physical manufacturing, ideal for rapid prototyping and custom creations.
Transform your simple picture into a sophisticated 3D design today!



